A bifunctional nanoplatform based on copper manganate nanoflakes for bacterial elimination via a catalytic and photothermal synergistic effect†
Abstract
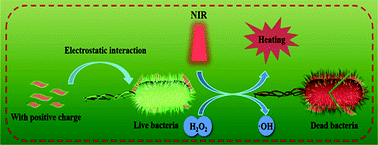
Bacterial infection has been recognized as one of the greatest threats to public health. In view of the continuous increase of bacterial resistance, constructing a collaborative bactericidal platform is a promising strategy to enhance the efficiency of antimicrobial agents. Herein, we report a facile, biocompatible and versatile nano-platform based on positively charged copper manganate nanoflakes (CuMnO2 NFs), which exhibits intrinsic peroxidase-like catalytic activity and excellent photothermal properties. The CuMnO2 NFs can bind with negatively charged bacteria via electrostatic interactions, and generate hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) through catalysis involving hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to make bacteria more susceptible to temperature. Introducing near-infrared light generates hyperthermia to fight against bacteria and enhances the peroxidase-like catalytic activity of the CuMnO2 NFs, thus producing more ˙OH to combat bacteria. The PTT-enhanced ˙OH synergistic antibacterial strategy exerts desirable antibacterial efficiencies of 98.78% and 99.92% against Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) at a controlled low temperature (below 50 °C), without damage to healthy tissues. Animal experiments indicate that this synergistic treatment has a better therapeutic effect on S. aureus-infected wounds in mice, compared with either treatment by itself. Therefore, this work holds great promise for developing new synergistic antimicrobial strategies to treat bacterial infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...