Deep-eutectic-solvent-based dispersive and emulsification liquid–liquid microextraction methods for the speciation of selenium in water and determining its total content levels in milk formula and cereals†
Abstract
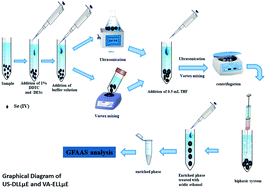
Rapid and environmentally friendly ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (US-DLLμE) and vortex assisted-emulsification liquid–liquid microextraction (VA-ELLμE) methods are proposed for the speciation of selenium in domestic and mineral water samples. A deep eutectic solvent (DES) prepared with different ratios of choline chloride and phenol is used as an extractant for hydrophobic tetravalent Se complexed with diethyldithiocarbamate in different water samples. The total inorganic Se species levels in water samples were determined via reducing Se(VI) to Se(IV), using sodium thiosulphate as a reducing agent. The total Se levels in formula milk and cereal samples were determined after microwave acid digestion. The different heating steps in GFAAS were also optimized. The analytical parameters for US-DLLμE and VA-ELLμE, including pH, the volume of complexing agent, the ultrasound and vortex mixing shaking times, and the volume and composition of the deep eutectic solvent, were optimized. The accuracies of both methods were confirmed based on the analysis of a certified reference material (CRM) BCR 189 (wholemeal flour). The enhancement factor (EF) and limit of detection (LOD) for Se(IV) via US-DLLμE were found to be 90.8 and 0.029 μg L−1, respectively, whereas an EF of 81.8 and LOD of 0.036 μg L−1 were obtained via VA-ELLμE. The % relative standard deviation (%RSD) values obtained based on the analysis of six replicate standards under the optimized conditions for US-DLLμE and VA-ELLμE were found to be 4.2 and 5.8%, respectively. The optimized methods were applied to different drinking water samples, and acid-digested milk formula and baby cereal food samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...