Fabrication of an electrochemical sensor based on metal–organic framework ZIF-8 for quantitation of silver ions: optimizing experimental conditions using central composite design (CCD)†
Abstract
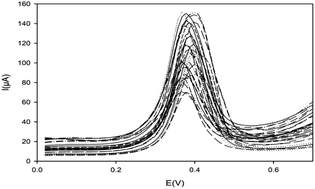
ZIF-8 was synthesized and carbon paste electrodes (CPEs) modified with this metal–organic framework were utilized for quantitation of silver(I) by the differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry (DPASV) technique.Prepared ZIF-8 and the matrix of the electrodes were distinguished by impedance spectroscopy (EIS), XRD, FT-IR spectroscopy, cyclic voltammetry (CV), TEM and SEM/EDX methods. To obtain the strongest stripping peak currents, several significant variables were optimized with response surface methodology (RSM), including the ligand amount (near 11% w/w), applied potential for preconcentration (approximately −1.36 V), pH of the preconcentration solution (about 8.5) and preconcentration time (about 275 s). A calibration curve was acquired in the limits from 1.0 × 10−10 to 5.0 × 10−7 M with the Pearson correlation coefficient R = 0.9993. The limiting detectable concentration (LDC) was determined to be 1.0 × 10−11 M. The developed sensor has high selectivity for mercury(II). The excellent pH, potential and especially size-exclusion based selectivity of the prepared sensor are unique characteristics that are very important in the determination of silver ions. The developed method was effectively employed for the quantitation of silver(I) ions in environmental and industrial samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...