A sensitive pH indicator-based spectrophotometric assay for PHB depolymerase activity on microtiter plates†
Abstract
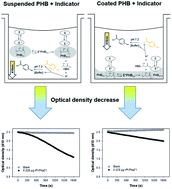
A continuous spectrophotometric assay for the screening of PHB depolymerase activity in microtiter plates was developed. We evaluated crystalline PHB in the suspension and coated it with the addition of a pH indicator to detect the breakage of the ester bond by proton titration. The reaction rate and the concentration of the recombinant PhaZ1 from Paucimonas lemoignei PHB depolymerase presented a linear correlation. A comparison of the proposed method with the turbidimetric method adapted to the microtiter plates revealed that the use of indicators increases the response signal by at least 5-fold, resulting in increased sensitivity and better signal-to-noise ratio. Furthermore, the proposed method offers a wide range of pH from 5.0 to 9.2 by using different buffer–indicator pairs and was employed for the screening of PHB-depolymerase activity on 140 bacterial strains isolated from Lake Chapala. Eleven strains were positive for PHB-depolymerase activity, which were ACSLRF-27, ACPLRF-6, and ACPLRF-5 (16S rRNA sequence alignment revealed 99–100% similarity with Actinomadura geliboluensis strain A8036, Streptomyces cavourensis strain NRRL 2740, and Streptomyces coelicolor strain DSM 40233, respectively); these that showed the highest activities. In conclusion, the method was successfully applied for finding new strains and for quantifying the PHB depolymerases activity with crystalline PHB.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...