Application of a magnetic nanocomposite of cross-linked poly(styrene/divinylbenzene) as an adsorbent for the magnetic dispersive solid phase extraction-dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of atrazine in soil and aqueous samples†
Abstract
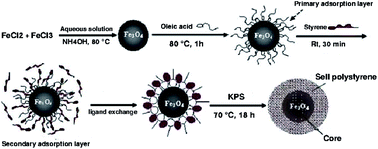
Magnetic polymeric nanocomposite particles were used as an adsorbent for the extraction of atrazine in soil and water samples. The authors combined magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction (MD-SPE) and dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) coupled with a gas chromatography-nitrogen phosphor detection for the preconcentration and determination of the analyte. Magnetic nanocomposites of cross-linked poly(styrene/divinylbenzene) (Fe3O4@PS/DVB-MNPs) with the mean size of about 60 nm were prepared by a mini-emulsion polymerization technique. The parameters affecting the extraction efficiency including the amount of adsorbent, absorption and desorption times, the volume of the elution (disperser) and extraction solvents, pH and volume of the sample solution, and salt concentration were optimized by a response surface methodology. Acetone was selected as the eluent in MD-SPE and disperser solvent in DLLME, and chlorobenzene was used as the extraction solvent. Under the optimized conditions, the enrichment factor was 750 and extraction recovery was 53%. The response was linear in the range of 0.05–450 μg L−1 with a determination coefficient of 0.9988. The limit of detection was 0.01 μg L−1. The intra-day and inter-day precisions of the method were in the range of 2.8–5.2% and 4.6–7%, respectively. The relative recovery of the method was in the range of 81–103% for the real samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...