Rapid identification of the “smart drug” modafinil in suspicious tablets by DART-HRMS combined with micropunching†
Abstract
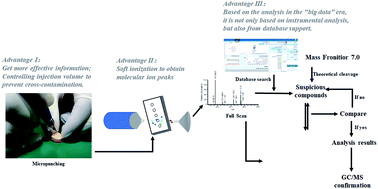
Recently, increasing numbers of imported parcels have contained tablets that have been mixed with others containing modafinil; thus, it is necessary to develop a rapid screening method for this compound. A rapid and accurate approach using direct analysis in real time coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry (DART-HRMS) and combined with the micropunching method was developed to detect modafinil. The effects of the injected concentration, ion source temperature and capillary temperature on the detection of modafinil by DART-HRMS combined with micropunching were evaluated. The optimized injection concentration of modafinil, ion source temperature and capillary temperature were determined to be 1 μg mL−1, 200 °C and 150 °C, respectively. DART-HRMS combined with micropunching can control the concentrations of target compounds in the seized modafinil tablets that are injected into an instrument, effectively avoiding the interference of dimer formation caused by excessive concentrations on the rapid identification of unknowns. This high-throughput approach was successfully applied to quickly identify seized modafinil tablets collected from authentic forensic cases, which was further confirmed by traditional gas chromatography-MS (GC-MS) techniques. The results demonstrated that DART-HRMS combined with micropunching is a useful approach for the rapid identification of suspicious modafinil tablets, allowing the detection and identification of modafinil with minimal sample preparation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...