Azithromycin electrochemical detection using a molecularly imprinted polymer prepared on a disposable screen-printed electrode
Abstract
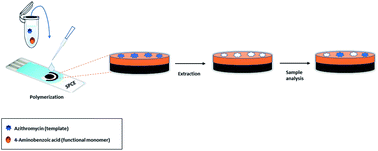
Azithromycin (AZY) is among the antibiotics with the highest concentrations in aqueous matrices. Conventional wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) do not fully remove this compound and it has been found in the environment. The health effects of AZY on humans and the environment are not yet understood. Therefore, the development of sensitive and selective analytical methods for AZY determination is important. In this work, an electrochemical molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) sensor was developed for the quantification of AZY. The selection of the functional monomer was performed by molecular modelling using quantum mechanics calculations. The MIP was electropolymerized by cyclic voltammetry (CV) on a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) using a solution containing 4-aminobenzoic acid (4-ABA) in the presence of AZY as a template molecule. The characterisation of the sensor was carried out using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), CV and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The analysis of AZY was performed by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) in the linear range between 0.5 and 10.0 μM, with a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.08 μM (S/N = 3) and a limit of quantification (LOQ) of 0.3 μM (S/N = 10). The MIP sensor was found to have selectivity to recognise AZY molecules and was successfully applied in the analysis of tap water and water samples collected upstream of a WWTP output in the Ave River. The proposed sensor presents a simple, selective and environmentally friendly strategy for AZY determination in environmental water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...