Mesoporous yolk–shell structure molecularly imprinted magnetic polymers for the extraction and detection of 17β-estradiol
Abstract
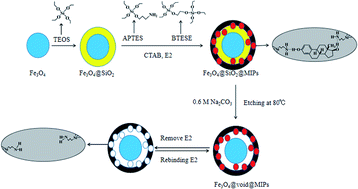
Novel mesoporous yolk–shell structure magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (MYS-MMIPs) were synthesized via surface polymerization using E2 as a template followed by chemical selective etching to remove the inorganic silica interlayer for the rapid, selective extraction and sensitive detection of 17β-estradiol (E2) in milk powder. For MYS-MMIPs, transmission electron microscopy coupled with N2 adsorption experiments confirmed the successful formation of a mesoporous yolk–shell structure. Furthermore, the thermogravimetric and recycling experiments showed the good thermal and adsorption stability of MYS-MMIPs, the magnetic properties experiment confirmed their good magnetic response, and the binding experiment indicated their selective recognition and high binding capacity (39.24 mg g−1) for E2. The obtained polymers were applied as adsorbents for the magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) of E2. After optimizing the MSPE conditions, an MSPE-HPLC method was developed for the determination of E2 in milk powder. The linear range was 1–300 μg kg−1 with a limit of detection of 0.33 μg kg−1. The satisfactory recoveries ranged from 88.3–102.4% and the relative standard deviations (RSDs) were lower than 5.5%. Thus, the MSPE-HPLC method has high accuracy and sensitivity for the analysis of E2 in milk samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...