Monitoring the effect of therapeutic doses of gamma irradiation on medulloblastoma by Raman spectroscopy
Abstract
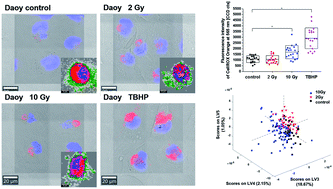
Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are the most common brain cancer treatment options determined by the type and the stage of the illness. Monitoring the effect of radiotherapy becomes as important as a cancer diagnosis. Within this context, the main goal of this study was to provide new insights into the monitoring of biochemical changes of medulloblastoma exposed to gamma irradiation with a low dose of 2 and 10 Gy using a label-free method (Raman microspectroscopy) and compare it with labelled techniques (metabolic activity and oxidative stress assays). Results showed that Raman spectroscopy can correctly classify the response of medulloblastoma cells to gamma irradiation with a specificity and sensitivity of 80.35% and 79.65%, respectively. Collected Raman spectra display measurable radiobiological effects that correlated with the dose of 2 and 10 Gy according to conducted multivariate statistical analysis. A CellROX Orange fluorescence probe was able to monitor the oxidative stress in live medulloblastoma cells post-irradiation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...