Rapid detection of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae using pH response based on vancomycin-modified Fe3O4@Au nanoparticle enrichment and the carbapenemase hydrolysis reaction†
Abstract
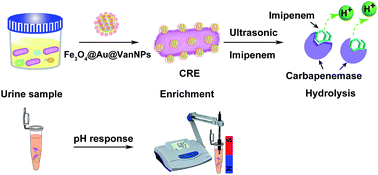
Rapid and simple detection of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) is important to manage infection and prevent the spread of these bacteria. In this work, we utilize pH response to detect CRE in urine rapidly. By using vancomycin-modified Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles (Fe3O4@Au@VanNPs), CRE in urine were enriched and separated efficiently via vancomycin–cell wall interaction. More importantly, carbapenemases released via CRE lysis were detected using a pH metre which responded to hydrogen ions generated from imipenem hydrolysis. Thus, the concentration of CRE in urine was detected via the carbapenemase hydrolysis reaction. The proposed method demonstrated a good linear relationship in the range of 104–108 cfu mL−1 for CRE with the limit of detection estimated to be 1.0 × 103 cfu mL−1. More importantly, this method successfully detected clinically isolated CRE strains in urine samples within 3.5 h. Thus, this biosensing strategy might have the potential for practical application in the rapid detection of various resistant bacteria.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...