Facile synthesis of a nanorod-like MoS2 nanostructure for sensitive electrochemical biosensing application†
Abstract
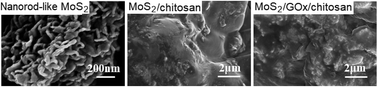
A novel nanorod-like MoS2 semiconductor nanostructure was synthesized through a simple two-step method. The nanorod-like MoS2 nanostructure was exploited as an electrode material to immobilize enzymes and for electrochemical sensing application. Characterization of the nanorod-like MoS2 nanostructure and the resultant biosensor was performed by scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and cyclic voltammetry. Enzyme molecules loaded at the MoS2 nanostructure retained their native structure and bioactivity. The direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase at the MoS2 nanostructure coated glassy carbon electrode was enhanced greatly. At an optimal potential of −0.45 V, the electrochemical glucose sensor had wide linear ranges of 1.5 × 10−5–3.25 × 10−4 M and 3.25 × 10−4–1.43 × 10−3 M, and a low detection limit of 0.005 mM (S/N = 3) with a high sensitivity of 25.06 ± 0.5 mA M−1 cm−2. At the same time, the present biosensor showed excellent selectivity, reproducibility and stability for glucose. What's more, the biosensor was successfully applied to the determination of practical samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...