Perturbation-induced high-frequency pulsing of nano-ESI with facile ion selection at atmospheric pressure†
Abstract
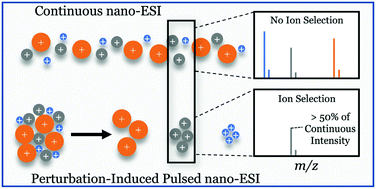
Nano-ESI is a commonly used ionization technique with continually expanding analytical advantages. Here, we report a facile way for high-frequency (500–3800 Hz) pulsing of nano-ESI, providing a high flux of mobility-selected ions. The pulsing is accomplished using a relatively low-voltage modulation (80 V peak-to-peak) of an electrode placed <1 cm downstream of a nano-ESI emitter biased to a constant potential. Configuring the electrode as an ion gate enables mobility-based ion selection by scanning the modulation frequency. Our investigations indicate that the electrode modulation perturbs continuous nano-ESI, resulting in solution accumulation at the emitter tip between spray pulses. Selective transmission of ions occurs at frequencies corresponding to harmonics of a fundamental frequency determined by the travel time of each ion from the emitter to the ion gate (pulsing electrode). Remarkably, the intensities of ions selected in this fashion are similar across the harmonics, suggesting that the ionization efficiencies of analytes have minimal dependence on the accumulated volume at the emitter tip. Moreover, intensities of ion-mobility-selected analytes using this technique reach >50% of those in continuous nano-ESI without ion selection, underscoring efficient ion generation via high-frequency pulsing. These findings indicate the potential of the pulsed nano-ESI for enhanced analytical utility, such as a high-flux selected-reagent-ion supplier at atmospheric pressure, and chart new avenues to further enhance the analytical performance of nano-ESI.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...