Plasmon induced deprotonation of 2-mercaptopyridine
Abstract
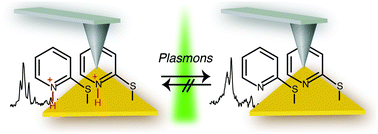
Surface plasmons can provide a novel route to induce and simultaneously monitor selective bond formation and breakage. Here pH-induced protonation, followed by plasmon-induced deprotonation of 2-mercaptopyridine was investigated using surface- and tip-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS and TERS). A large difference in the deprotonation rate between SERS and TERS will be demonstrated and discussed with respect to hot-spot distribution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...