Environmental distribution of the neurotoxin l-BMAA in Paenibacillus species
Abstract
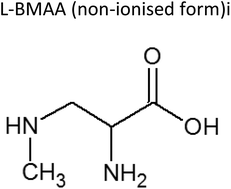
The environmental distribution of the neurotoxic amino acid, 3-N-methyl-2,3-diaminopropanoic acid (BMAA), first isolated in 1967, was initially believed to be limited to tropical and subtropical plants of the genus Cycas. The seeds of one such species, which had been used historically on the Pacific island of Guam as a foodstuff, had a reputation for neurotoxicity. Some 40 years later the amino acid was detected in terrestrial and aquatic cyanobacteria and in other aquatic organisms. Overlooked was the discovery of BMAA in peptides of bizarre structure that had been isolated in 1975 from Paenibacillus pulvifaciens during a search for antibiotics. More recently (2014), peptides of similar structure were isolated from Paenibacillus larvae; this organism is causative of American Foulbrood, a lethal disease of honeybee colonies. These are interesting chemical and environmental observations, but knowledge of the bacterial distribution of BMAA is limited to just these two species of Paenibacillus, while more than 200 Paenibacillus spp. are known. Paenibacillus spp. are ever present naturally in the environment and are used agriculturally; recent research reports that some species infect human foods – including cow's milk – and have been isolated from human body fluids. We wish to stimulate interest in the environmental distribution of the neurotoxic BMAA in Paenibacillus spp. by drawing together previously isolated streams of research and by proposing experimental approaches by which this matter might be resolved.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...