Direct observation of reverse intersystem crossing from fully confined triplet exciplexes using magneto-electroluminescence†
Abstract
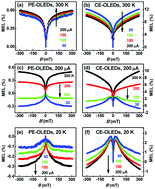
Because of efficient triplet harvesting for high external quantum efficiency of light emission, exciplex-based organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) have been studied recently. Their magneto-electroluminescence (MEL) traces are positive and show normal current dependence. Surprisingly, herein, negative MEL curves were observed from red light-emission exciplex-based OLEDs because the low-energy triplet charge transfer states within these devices were fully confined. The MEL traces from these red light-emission exciplex-based OLEDs exhibited various unusual behaviors, which indicated reverse intersystem crossing. These behaviors were: (i) abnormal current dependence of the positive MEL traces at ambient temperature, which increased in intensity at higher injection currents; (ii) an unprecedented positive-to-negative sign conversion of the MEL at ∼100 K as the temperature decreased; (iii) anomalous current-dependence of all negative MEL traces at 20 K. Moreover, when spacer layers with different thicknesses were inserted between the donor and acceptor materials in the exciplex-based OLEDs, excimer emission and ambient-temperature triplet–triplet annihilation processes were observed, which indicated that the excimers had long emission lifetimes. This work provides considerable insight into the physical mechanisms of intersystem crossing and reverse intersystem crossing in exciplex-based OLEDs, and triplet–triplet annihilation, in excimer-based OLEDs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...