Temperature dependent energy transfer in Bi/Er codoped barium gallogermanate glasses for tunable and broadband NIR emission
Abstract
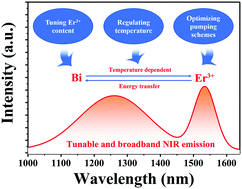
Bi-Doped glasses and fibers show tremendous potential for application in broadband optical amplifiers and tunable fiber lasers due to their intriguing broadband near infrared (NIR) luminescence. However, it is unfortunate that most Bi NIR emissions suffer from a low intensity at C and L telecommunication bands. In this work, a broadband NIR luminescence with improved emission intensity of C and L bands is realized in Bi/Er codoped barium gallogermanate glasses, which has been proved to be a suitable matrix for Bi fiber preparation. The energy transfer between Bi NIR emission centers and Er3+ is confirmed and the energy transfer efficiency from the Bi NIR emission centers to Er3+ increases by 6 times as the Er3+ content is increased from 0.5 to 2 mol%. As the temperature increases from 10 to 393 K, Bi emission in Bi/Er codoped glass shows a further decrease in comparison to that in Bi singly doped glasses. This indicates that the energy transfer from the Bi NIR emission centers to Er3+ could be enhanced by increasing the temperature. Moreover, the dependence of the NIR emission intensity on excitation and the emission wavelength in Bi/Er codoped barium gallogermanate glasses was investigated, providing diverse pumping schemes to excite the Bi NIR emission centers and Er3+ in parallel. Hence, by tuning the Er3+ content, regulating the temperature and optimizing the pumping schemes, a tunable and further broadened NIR emission can be achieved in Bi/Er codoped barium gallogermanate glasses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...