Mechanical properties and electromagnetic shielding performance of single-source-precursor synthesized dense monolithic SiC/HfCxN1−x/C ceramic nanocomposites†
Abstract
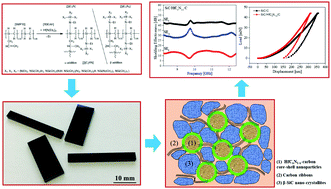
For the first time, single-source-precursor synthesized dense monolithic SiC/HfCxN1−x/C ceramic nanocomposites with outstanding electromagnetic (EM) shielding performance at temperatures up to 600 °C are reported. The total shielding effectiveness (SET) of the SiC/HfCxN1−x/C monolith is >40 dB at 600 °C, which is superior than most of the reported EM shielding materials under the same conditions. Compared with a Hf-free SiC/C monolith, the SiC/HfCxN1−x/C monolith possesses superior EM shielding performance due to the presence of a highly conductive HfCxN1−x phase. Moreover, the HfCxN1−x-particles are covered by a carbon layer forming core–shell nanoparticles connected with graphite-like carbon ribbons, which result in electrically conductive networks within the semiconducting β-SiC matrix. In addition, the hardness, Young's modulus and flexural strength of the dense SiC/HfCxN1−x/C monolith are measured to be 29 ± 4 GPa, 381 ± 29 GPa and 320 ± 25 MPa, respectively. The outstanding EM shielding performance combined with excellent mechanical properties of the dense monolithic SiC/HfCxN1−x/C nanocomposites provides a novel strategy to fabricate EM shielding materials for applications in harsh environments and/or under high mechanical load.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...