Solid-state silicon nanoparticles with color-tunable photoluminescence and multifunctional applications†
Abstract
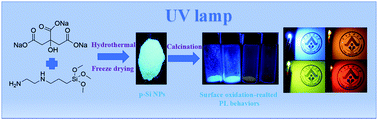
In this paper, a facile hydrothermal route was proposed to synthesize a bright blue-emitting solution of silicon nanoparticles (s-Si NPs) with a high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) of 66%. And a self-quenching-resistant solid-state fluorescent powder of Si NPs (p-Si NPs) was obtained by freeze drying, which exhibited dual wavelengths with blue and yellow emission peaks. In addition, the blue-band emission of p-Si NPs was ascribed to the graphitizing cores, while the yellow-band emission of p-Si NPs originated from the trapping surface state. Based on this finding, a high temperature calcining strategy was proposed to obtain multicolor Si NP powders by adjusting the surface defects of p-Si NPs for the first time. A series of multicolor Si NP powders with wavelengths from blue to red was obtained by adjusting the calcination time/temperature. Structural and spectroscopic characterizations also proved that the mechanism of their PL red shift was attributed to the oxygen-related surface state, rather than the size effect. Because of their unique multicolor emission, their related multicolor light-emitting diode (LED) devices were obtained to explore their possible application in the field of solid-state lighting. Moreover, SSF-2-based films were fabricated by combining carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and SSF-2 powder to explore their potential application as light conversion films (LCFs) in the field of agricultural planting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...