Modification of the p-GaP(001) work function by surface dipole bonds formed in sulfide solution†
Abstract
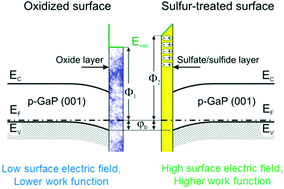
Modification of the surface chemical composition and electronic structure of the native-oxide-covered p-GaP(001) surface by treatment with sulfide solution is studied by high-resolution synchrotron photoemission spectroscopy (SXPS) and reflectance anisotropy spectroscopy (RAS). Treatment of the p-GaP(001) surface with a solution of ammonium sulfide in 2-propanol causes removal of the native oxide layer and formation of a passivating layer consisting mainly of gallium sulfides and sulfates. The latter species are formed due to oxidation of sulfides with hydroxyl groups existing in the solution. After such a treatment the downward surface band bending of about 0.5 eV remains essentially unaffected, while the electronic work function increases by 0.6 eV indicating modification of the surface dipole. As a result, the valence band maximum at the surface shifts to 5.6 eV. In reflectance anisotropy spectra the surface dipole modification produces an essential increase of the anisotropy signal in the spectral region of the direct optical transition point E1 indicating considerable increase of the near-surface electric field. This dipole-induced near-surface electric field remains essentially unchanged on air exposure of the sulfur-treated p-GaP(001) surface for at least 6 months.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...