Using ultra-fast spectroscopy to probe the excited state dynamics of a reported highly efficient thermally activated delayed fluorescence chromophore†
Abstract
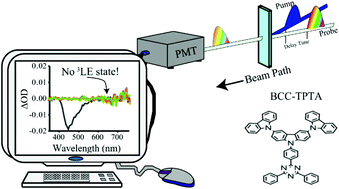
Multiple ultrafast spectroscopic techniques and quantum chemical simulations (QCS) were used to investigate the excited state dynamics of BCC-TPTA. This organic chromophore is believed to possess excited state dynamics governed by a thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) mechanism with a reported internal quantum efficiency (ηIQE) of 84%. In addition, a significant enhancement in its quantum yield (Φ) in solution after purging oxygen has been reported. This Φ enhancement has been widely accepted as due to a delayed fluorescence process occurring on the μs time-scale. The spectroscopic measurements were carried out both in solution and blended films, and from fs to μs time-scales. The excited state dynamics of Rhodamine B and Ir(BT)2(acac) were also probed for comparison. Investigations in the absence of oxygen were also carried out. Our time-correlated single photon counting (TCSPC) measurements revealed a lack of a long-lived emissive lifetime for BCC-TPTA in any of the media tested. Our ns transient absorption spectroscopy (ns TAS) experiments revealed that BCC-TPTA does not possess triplet transient states that could be linked to a delayed fluorescence process. Instead, the evidence obtained from our spectroscopic tools suggests that BCC-TPTA has the excited state dynamics of a typical fluorescence chromophore and that just comparing the Φ difference before and after purging oxygen from the solution is not an accurate method to claim excited state dynamics governed by a delayed fluorescence mechanism. Consequently, we believe that previous studies, in which the photo-physics of organic chromophores with TADF characteristics are reported, may have overlooked the influence of the host materials on the obtained optical properties in blended films.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...