Novel nanoparticles of cerium-doped zeolitic imidazolate frameworks with dual benefits of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory functions against periodontitis
Abstract
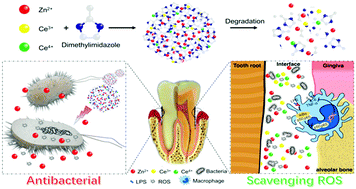
Periodontitis is a common bacteria-borne inflammatory disease that can damage the supporting structures of teeth, eventually leading to tooth loss and systemic inflammations. The present study developed novel nanoparticles (ZIF-8:Ce) by doping cerium (Ce) into zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) to simultaneously obtain antibacterial and anti-inflammatory capabilities. The objectives of this study were to: (1) develop novel ZIF-8 nanoparticles doped with different Ce/(Ce + Zn) molar ratios of 1%, 5% and 10% to combat periodontitis; (2) investigate the inhibition efficacy of different nanoparticles against biofilms of periodontal pathogens; and (3) evaluate the effects of different ZIF-8:Ce on inflammatory secretion and macrophage polarization in vitro. The results showed that Ce doping at a ratio from 1% to 10% did not compromise the regular and uniform structure of ZIF-8. ZIF-8:Ce possessed a sustained Zn2+ and Ce3+/Ce4+ release and favorable superoxide dismutase/catalase activities without cytotoxicity at a concentration below 30 μg mL−1. ZIF-8 exhibited an excellent anti-biofilm function against periodontal pathogens. Although 10% Ce doping into ZIF-8 slightly reduced the antibacterial effects, the CFU reduction still remained at approximately 2 orders of magnitude. More importantly, ZIF-8:Ce exhibited increasing anti-inflammatory effects with increasing amounts of Ce doping. In addition, ZIF-8:Ce10% exerted much better anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting pro-inflammatory factor expression via restraining the NF-kB/p65 subunit translocation (p < 0.05). Meanwhile, ZIF-8:Ce10% elevated the polarization of the M2 phenotype of macrophages and promoted anti-inflammatory cytokine secretion. Therefore, the novel ZIF-8:Ce nanoparticles provided a unique insight into the development of effective anti-inflammatory and antibacterial platforms for treating periodontitis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...