The preparation of oxidized methylcellulose crosslinked by adipic acid dihydrazide loaded with vitamin C for traumatic brain injury†
Abstract
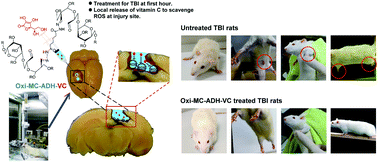
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is defined as the destruction or degeneration of brain cells due to external force. Free radical generation from the damage site is the major factor that causes post-therapeutic failure in TBI patient. In this study, an oxi-methylcellulose-adipic acid dihydrazide (oxi-MC-ADH) hydrogel was prepared as a vitamin C carrier for TBI in emergency that continuously releases vitamin C at the injured site in the brain. The results show that the oxi-MC-ADH hydrogel exhibits adequate gelation time and good biocompatibility in vitro. Vitamin C incorporated in the oxi-MC-ADH hydrogel (oxi-MC-ADH-VC) initially burst released in the first 6 h to serve as a primary treatment and then extendedly released for the secondary treatment. The analysis of gene expression and reactive oxygen species production was done to demonstrate the neuroprotective effects of the hydrogel. In vivo neurological function assays and behavioral tests show a significant improvement in the outcome in rats with TBI 3 weeks after the oxi-MC-ADH-VC hydrogel injection. This study demonstrates that the oxi-MC-ADH-VC hydrogel has a great potential in the management of TBI.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...