A postmodification strategy to modulate the photoluminescence of carbon dots from blue to green and red: synthesis and applications†
Abstract
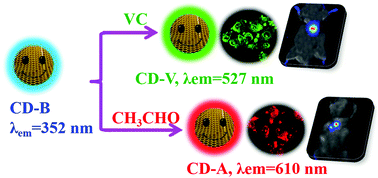
Carbon dots (CDs) have attracted increasing attention in bioimaging and theranostics because of their unique merits including small size, high photostability, good biocompatibility and excellent hydrophilicity. However, it is still challenging to tune the wavelength of CDs, especially long-wavelength emissive CDs. Herein, blue fluorescent CDs (named as CD-B) were synthesized via a hydrothermal route. In order to modulate the optical properties of CD-B and achieve a deeper level of biomedical applications, two convenient reactions of CD-B with Vitamin C and acetaldehyde were employed. It is very gratifying to see that green (named as CD-V) and red (named as CD-A) fluorescent CDs were obtained with the maximum emission at 527 nm and 610 nm, respectively. Compared to CD-B, the emission wavelength redshifts up to 175 nm and 285 nm, respectively. The superiorities of CD-V and CD-A such as excellent optical properties and good biocompatibility enable them to act as promising candidates for bioimaging. This work develops a simple postmodification strategy to tune the photoluminescence of CDs and opens up a new avenue for their modification and applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...