Near-infrared fluorescent probes based on TBET and FRET rhodamine acceptors with different pKa values for sensitive ratiometric visualization of pH changes in live cells†
Abstract
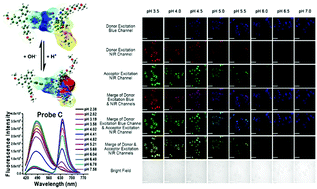
Three near-infrared ratiometric fluorescent probes (A–C) based on TBET and FRET near-infrared rhodamine acceptors with different pKa values were designed and synthesized to achieve sensitive ratiometric visualization of pH variations in lysosomes in visible and near-infrared channels. Tetraphenylethene (TPE) was bonded to near-infrared rhodamine dyes through short electrical π-conjugation linkers to prevent an aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ) effect and allow highly efficient energy transfer of up to 98.9% from TPE donors to rhodamine acceptors. Probes A–C respond to pH variation from 7.4 to 3.0 in both buffer solutions and live cells with significant decreases of donor fluorescence and concomitant extraordinary increases of rhodamine acceptor fluorescence because of highly efficient energy transfer. In addition, probe C is capable of determining pH fluctuations in live cells treated with chloroquine. The probes show good photostability, excellent cell membrane permeability, high selectivity to pH, and two well-resolved emission peaks to ensure accurately comparative and quantitative analyses of intracellular pH changes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 Journal of Materials Chemistry B Most Popular Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...