Tolerance to carbon corrosion of various carbon structures as catalyst supports for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells†
Abstract
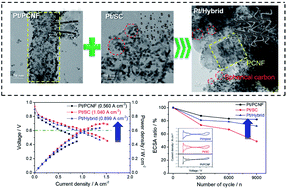
To overcome the stability issue at high voltages related to the carbon corrosion of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells, different types of platelet carbon nanofibers (PCNFs) featuring a wide range of fiber stems are employed as a Pt catalyst supporting material. Further, PCNFs are hybridized with spherical activated carbons (SC) as a Pt support to improve the electrocatalytic activity of the catalysts by increasing the surface area and electrical conductivity with well-distributed meso- and macro-pores, while maintaining tolerance to carbon corrosion of electrocatalysts. Tafel slopes of the catalysts for the kinetic current of electrocatalysts are in the order of Pt/PCNF (−58.2 mV dec−1) < Pt/Hybrid (−57.0 mV dec−1) < Pt/SC (−54.3 mV dec−1), showing the rapid kinetics of Pt/SC and Pt/Hybrid for the oxygen reduction reaction. The Pt catalysts are subjected to accelerated stress tests (AST) in which the cell voltage is cycled between 1.0 and 1.5 V in 2 s (1 cycle), and the Pt/PCNF and Pt/Hybrid catalysts are highly durable in carbon-corrosion durability testing. Furthermore, the MEAs with the Pt/PCNF, Pt/SC, and Pt/Hybrid catalysts are operated at 65 °C, and the maximum power densities of MEAs were 0.708, 0.674, and 0.507 W cm−2 for Pt/SC, Pt/Hybrid, and Pt/PCNF, respectively, as is consistent with the characteristics of catalysts. The MEAs are also subjected to AST at 80 °C, and a relatively small performance decay occurred at 0.6 V for the Pt/PCNF (36.2%) and Pt/Hybrid MEAs (44.0%), but considerably more degradation was observed for Pt/SC MEA (73.2%), signifying that the mechanochemically durable PCNF effectively prevented carbon corrosion with Pt agglomeration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...