UV-vis-IR irradiation driven CO2 reduction with high light-to-fuel efficiency on a unique nanocomposite of Ni nanoparticles loaded on Ni doped Al2O3 nanosheets†
Abstract
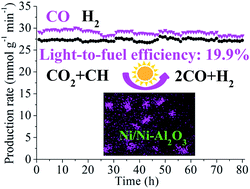
A unique nanocomposite of Ni nanoparticles loaded on Ni doped Al2O3 nanosheets (Ni/Ni-Al2O3) was prepared with a facile approach. Ni/Ni-Al2O3 possesses very high photothermocatalytic activity for CO2 reduction with CH4 (CRM) under focused UV-vis-IR irradiation. Its production rates of H2 and CO (rH2 and rCO) are 27.02 and 28.71 mmol g−1 min−1, respectively. A very high light-to-fuel efficiency (η) of 19.9% is achieved. Even under focused vis-IR irradiation of λ > 690 nm, it still possesses photothermocatalytic performance, evidenced by its high rH2 and rCO values (14.64 and 17.24 mmol g−1 min−1) and a high η value of 16.4%. Ni/Ni–Al2O3 possesses excellent photothermocatalytic durability which is much superior to its counterpart of Ni nanoparticles loaded on Al2O3 nanosheets (Ni/Al2O3). This is ascribed to the synergetic effect between Ni nanoparticles and Ni doped Al2O3 in Ni/Ni-Al2O3 in which oxygen in Ni doped Al2O3 participates in the oxidation of the formed carbon species, thus inhibiting carbon deposition on Ni nanoparticles. The high photothermocatalytic activity of Ni/Ni-Al2O3 originates from effective light-driven thermocatalytic CRM. A new type of photoactivation is discovered to substantially reduce the activation energy for CRM on Ni/Ni-Al2O3, thus considerably enhancing the light-driven thermocatalytic activity. Moreover, the new photoactivation also substantially inhibits the CO disproportionation side reaction, thus promoting the photothermocatalytic durability due to carbon deposition being substantially reduced.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...