Reversible modulation of photoenergy in Sm-doped (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 transparent ceramics via photochromic behavior†
Abstract
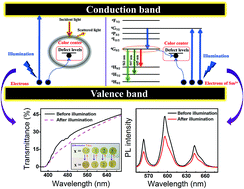
By simply doping with a certain amount of Sm3+, opaque lead-free (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 piezoelectric ceramics were fabricated into transparent/translucent ceramics. The photochromic (PC) behavior and associated reversible transmittance/luminescence modulation were realized via physical means. Upon illumination under a xenon lamp, the maximal decreased values of optical transmittance and luminescence intensity are 36.1% and 49%, respectively. Meanwhile, the colors of all the ceramics turn darker after illumination, and subsequently return to their initial states by thermal stimulus (200 °C for 5 minutes), exhibiting a typical PC phenomenon. Combining experimental and calculation results, it can be found that the PC mechanism is closely related to the vacancy defects induced by both high-temperature sintering and Sm3+-doping. Additionally, the Sm3+ effects on phase structures, microstructures, optical transmittance and photoluminescence properties of the ceramics were systematically studied. The substitution behavior of Sm3+ and vacancy defect concentrations on the energy band gap of the material were unraveled by the first principles calculations to further clarify the corresponding mechanism. The Sm3+-doped (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 transparent ceramics have potential for application in modulation and conversion of photoenergy, such as in optical memory and photo-switching devices. And the reversible tuning of transmittance in our material is especially attractive for exploring novel transparent PC materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...