A general strategy to prepare high-quality inorganic charge-transporting layers for efficient and stable all-layer-inorganic perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
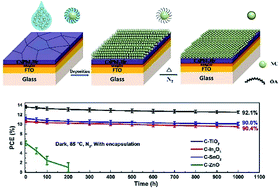
Due to the drawbacks of long-term instability encountered in organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite solar cells (PSCs), building all-layer-inorganic PSCs composed completely of an inorganic perovskite absorber layer and inorganic charge-transporting layers (CTLs) has attracted increasing interest, due to removal of thermally unstable organic components. To do this, one of the greatest challenges lies in the deposition of efficient and stable inorganic CTLs on top of perovskites. Here, a general strategy, i.e., depositing monodisperse nanocrystals followed by a special thermal treatment, has been proposed to fabricate high-quality carbide–metal oxide (C–MOX) CTLs on top of the inorganic perovskite of CsPbI2Br. Effects of the energy levels, conductivities and chemical stabilities of different CTLs on the efficiency and long-term stability of their corresponding PSCs have been systematically studied. It has been found that the inverted CsPbI2Br PSC based on C–TiO2 yields the highest power conversion efficiency of up to 14.0%, mainly attributed to its best interfacial band alignment and suitable conductivity, and except those based on C–ZnO with lower chemical resistance to halide perovskites, all-layer-inorganic PSCs present excellent stabilities, and could retain >90% of their initial PCEs after aging at 85 °C in the dark and under continuous light-soaking at 45 °C for 1000 hours.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...