Hybrid electrolyte enables safe and practical 5 V LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 batteries†
Abstract
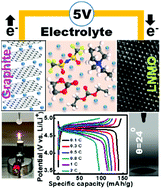
Bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide (TFSI)-based ionic liquid (IL) has high thermal and electrochemical stability, but it is not an ideal battery electrolyte due to the poor rate capability of cells that use it, problematic anode compatibility, and high cost. The incorporation of a carbonate solvent could mitigate these problems, but it would also lead to serious Al current collector corrosion at high potential. This long-existing problem is overcome in this study by modulating the LiTFSI concentration and IL/carbonate ratio in the hybrid electrolyte. The Al corrosion and electrolyte decomposition side reactions at 5 V (vs. Li+/Li) can be suppressed in 3 M LiTFSI 25%-IL electrolyte, in which good performance of a high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 (LNMO) cathode is achieved. Capacities of 140 and 88 mA h g−1 were measured at 0.1 and 2C, respectively (vs. 25 mA h g−1 at 2C for a plain LiTFSI/PMP–TFSI IL electrolyte). After 300 charge–discharge cycles, 90% of the initial LNMO capacity was retained. This electrolyte also shows low flammability and great wettability toward a polyethylene separator. Moreover, this electrolyte allows elevated-temperature storage and operation of LNMO cells at 55 °C, which is not possible with the conventional carbonate electrolyte. Good compatibility of the electrolyte with a graphite anode is also demonstrated. The proposed electrolyte design concept has great potential for next-generation 5 V Li-ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...