Gaseous CO and toluene co-oxidation over monolithic core–shell Co3O4-based hetero-structured catalysts†
Abstract
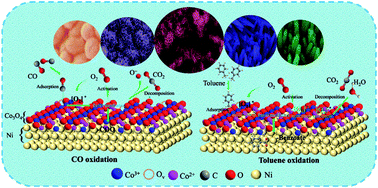
The inhibiting effects of using platinum group metal (PGM) catalysts are universal problems for the co-oxidation of CO and hydrocarbons (HCs), resulting in a higher temperature to handle CO and HCs pollutants. Herein, this work focuses on designing a series of Co3O4-based catalysts whose catalytic activities in the individual oxidation and co-oxidation of CO and toluene are comparable to Pt-based catalysts. The catalytic behaviors of CO and toluene oxidation over Pt/Al2O3 are mutually inhibited in the presence of CO and toluene, in which CO oxidation could improve catalytic toluene degradation over Co3O4-based catalysts, as its CO oxidation is negatively affected by toluene oxidation. In addition, under the coexistence of CO and toluene, the light-off temperature of toluene oxidation on both Co3O4-based and Pt-based catalysts consistently followed that of CO oxidation. Among all monolithic core–shell Co3O4-based catalysts, these catalysts introduced to different elements (Co, Mn and Cu) showed the distinct promotion of CO and toluene oxidation, and the Co3O4@Co3O4 catalyst exhibited the most outstanding catalytic performances for the individual oxidation and co-oxidation of CO and toluene. In addition, the physicochemical properties of core–shell hetero-structured catalysts are further characterized in detail by XRD, BET, SEM, TEM, H2-TPR, XPS, O2-TPD and Raman spectrometry. It was confirmed that the excellent performance of the Co3O4@Co3O4 catalyst is mainly associated with the surface area, surface oxygen vacancies and low-temperature reducibility, whose prominent oxygen vacancy and low-temperature reducibility are induced by the synergistic effect of different Co3O4 structures. In situ DRIFT spectroscopy confirmed that bidentate carbonate species and benzoate species were considered as a reaction intermediate species in CO and toluene oxidation, respectively. Moreover, there is a competitive adsorption-reaction on the active sites of Co3O4-based catalysts for CO and toluene, but the reaction mechanism of CO/toluene oxidation may be mutually independent under the coexistence of CO and toluene.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...