Anti-biofouling double-layered unidirectional scaffold for long-term solar-driven water evaporation†
Abstract
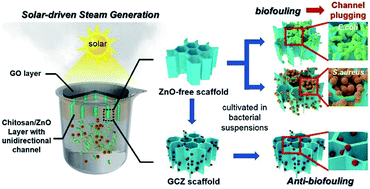
To meet the demand for clean water, solar-driven water evaporation has recently drawn growing attention due to the high efficiency and environment-friendly procedure. For the transportation of water, these evaporation devices mostly possess porous structures. However, for long-term use in the natural environment, it is highly required to prevent biofouling induced channel plugging due to the universal existence of microbes in the natural water. Herein, we fabricated a double-layered GO–chitosan/ZnO scaffold (GCZ scaffold) as the solar steam device. The upper GO aerogel layer serves as a solar thermal converter, while the lower chitosan/ZnO composite layer serves as a unidirectional water pump. This GCZ scaffold exhibits a high water evaporation rate and good solar energy conversion efficiency under 10 sun and one sun irradiations, respectively. Moreover, the embedding of ZnO nanoparticles in the lower chitosan layer effectively controls the formation of biofilms in the unidirectional channels, resulting in an anti-biofouling solar-driven water evaporator. Compared to the ZnO-free scaffold suffering from the biofouling induced channel plugging, this anti-biofouling GCZ scaffold maintains a high solar-driven water evaporation rate and efficiency (89.4% for E. coli and 89.7% for S. aureus) even after cultivating in the bacterial suspensions for 3 days. This anti-biofouling solar-driven water evaporator evidently improves the lifetime of the material in natural water, conducive to further commercial applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...