Local Li-ion conductivity changes within Al stabilized Li7La3Zr2O12 and their relationship to three-dimensional variations of the bulk composition†
Abstract
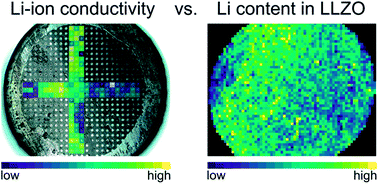
The attractiveness of cubic Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO) based garnets lies in their high ionic conductivity and the combination of thermal and electrochemical stability. However, relationships between the exact chemical composition and ionic conductivity are still not well understood and samples of very similar composition and processing may show very different properties. In this contribution, we investigated Al stabilized LLZO by employing a combination of local conductivity measurements and 3D local chemical analysis using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (LA-ICP-OES). These measurements revealed significant conductivity variations across some samples, with variations up to almost one order of magnitude, as well as an inhomogeneous elemental distribution of Al and Li, largely along the samples. Surprisingly, neither the local Al content nor the local Li content showed a clear correlation with the local Li-ion conductivity. Accordingly, an in-depth understanding of the conduction properties of Al stabilized LLZO has to concentrate on aspects beyond the simple chemical composition. Yet unknown factors (e.g. oxygen vacancies or local cation site occupancies) seem to have a much higher impact on the ionic conductivity than the exact stoichiometry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...