Fabrication of hollow pompon-like Co3O4 nanostructures with rich defects and high-index facet exposure for enhanced oxygen evolution catalysis†
Abstract
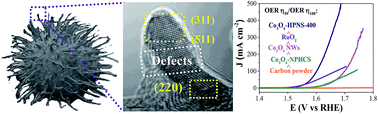
In recent years, developing effective methods to enhance the properties of Co3O4 nanomaterials for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) has received considerable attention. However, the reported methods focused on fabricating nanostructures with one of the catalytically favorable structural factors, such as exposed facets, oxygen vacancies, morphology, or size. Herein, a unique method was developed to construct a Co3O4 nanostructure with high OER catalytic performance by integrating various catalytically favorable factors into the nanomaterial, such as a unique hollow morphology with a large surface area, abundant pores, rich defects and exposed high-index facets. Here, hollow pompon-like Co3O4 nanostructures (Co3O4-HPNSs) were controllably synthesized through a self-assembled encapsulation-calcination method. The fabricated nanostructure calcinated at 400 °C (Co3O4-HPNS-400) exhibits a high surface area of 233.5 m2 g−1 with a pore volume of 0.55 cm3 g−1. Surprisingly, the unique structure is rich in Stone–Wales-like defects and high-index facets of (311), (511) and (220). Due to these catalytically active structural characteristics, the fabricated Co3O4-HPNS-400 showed overpotentials of 308, 320, 348, and 370 mV for the OER at the current densities of 10, 20, 50 and 100 mA cm−2, respectively, which are lower than those of Co3O4 nanowires (Co3O4-NWs). This study provides an efficient method to fabricate unique Co3O4 nanostructures with enhanced catalytic activity for the OER.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...