Framework Cu-doped boron nitride nanobelts with enhanced internal electric field for effective Fenton-like removal of organic pollutants†
Abstract
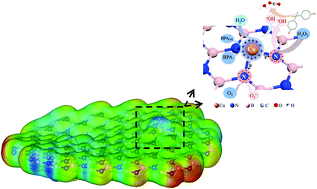
Framework Cu-doped boron nitride nanobelts (Cu-BN) were synthesized via a facile pyrolysis method. XPS and EXAFS fitting results demonstrated that Cu existed in the form of Cu–N bonds in the Cu-BN framework, in a raised position on the plane network of the bulk BN. Experimental and theoretical studies verified that the framework incorporation of Cu led to the formation of an internal electric field due to the nonuniform electron distribution with electropositive Cu sites and electronegative N sites. This unique structure promoted the reduction of H2O2 on the electronegative N sites and the oxidation of H2O on the electropositive Cu sites to generate highly aggressive ˙OH, accelerating the degradation of pollutants adsorbed on Cu-BN. On the other hand, organic pollutants can donate electrons to Cu by the π → Cu(II) interaction in the σ–Cu–ligand complexes between phenolic groups and surface Cu, accompanied by the oxidation of pollutants, as confirmed by solid EPR. As a result, various refractory pollutants could be efficiently degraded and mineralized in the Cu-BN/H2O2 system over a wide pH range of 3–11. Moreover, high H2O2 utilization efficiency was obtained, with the production of 1.46 mol ˙OH radicals from per mol H2O2 in the first 15 min, much higher than that (0.1–0.6 mol) in traditional systems. This study indicates that the construction of an internal electric field through tuning the electron distribution of catalysts is feasible and effective in Fenton-like reactions for water environmental remediation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...