Ultra-high performance of Li/Na ion batteries using N/O dual dopant porous hollow carbon nanocapsules as an anode†
Abstract
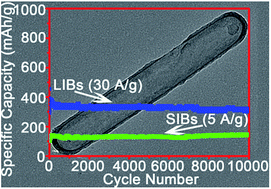
Carbon materials usually exhibit a low capacity, short cycle life and poor rate performance as anode materials for lithium ion batteries (LIBs) and sodium ion batteries (SIBs). It remains a great challenge to explore carbon materials for ultrafast lithium and sodium storage with both a high capacity and a long cycling stability. Herein, we report the fabrication of nitrogen (N)/oxygen (O) dual dopant hollow porous carbon nanocapsules that show a state-of-the-art electrochemical performance. If used as anodes for LIBs, at an ultrahigh current density of 30 A g−1, the carbon nanocapsules can be cycled up to 11 000 cycles with a considerable capacity retention of ∼310 mA h g−1. For sodium storage, they also demonstrate an ultrastable cycling performance with a reversible capacity of ∼150 mA h g−1 after 10 000 cycles at a high current density of 5 A g−1. The outstanding electrochemical performance can be ascribed to the synergistic effects from heteroatom doping and the unique sealed porous hollow characteristics of the nanocapsules. Theoretical calculations suggest that the sealed capsule structure leads to a excellent mechanical stability, which can tolerate fast lithium/sodium intercalation and extraction at ultrahigh current densities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...