Interfacial assembled preparation of porous carbon composites for selective CO2 capture at elevated temperatures†
Abstract
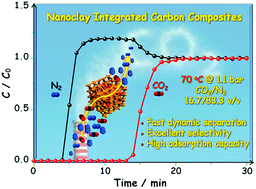
Development of porous sorbents that can selectively capture carbon dioxide (CO2) through adsorption technology from the flue gas is essential to reduce emission of CO2 to the atmosphere. However, under typical flue gas conditions (∼0.15 bar of CO2 at 40–70 °C), the adsorption capacity and selectivity for CO2 over those for nitrogen (N2) remain poor on traditional porous adsorbents due to weak adsorbent–adsorbate interactions. Here, we report the synthesis of hierarchically structured porous carbon composites via an interfacial assembling strategy using nanoclay LAPONITE®, resorcinol and formaldehyde as the precursors. This fabrication strategy allows fine tuning of the surface chemistry and pore network of porous carbons with the aim of enhancing the CO2 capture capacity at elevated temperatures (e.g., 50–150 °C). The obtained carbon composites reach a record-high CO2/N2 selectivity (114.3) at 70 °C, according to equilibrium gas adsorption analysis and dynamic breakthrough measurement associated with a high adsorption capacity of 1.7 mmol g−1 at 1.1 bar and 70 °C, and 0.5 mmol g−1 at 0.17 bar and 70 °C. The inorganic substance integrated 3D carbon framework is responsible for such superior CO2 capture at 70 °C by enhancing adsorbent–adsorbate interactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...