Solid-state polymer electrolytes stabilized by task-specific salt additives†
Abstract
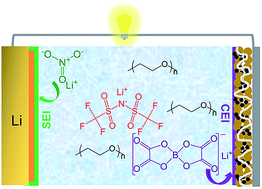
Solid state electrolytes (SSEs) are actively studied for their potential to markedly enhance the safety and performance features of high-energy rechargeable batteries that utilize reactive metals (Li, Na, etc.) as anodes. Electrochemical cell designs in which the metal anode is coupled with a conventional, intercalating cathode such as lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide (NCM), lithium cobalt oxide (LCO), or lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide (NCA), are of immediate interest both because of gains in specific energy and the inherent simplicity of solid-state battery designs enabled by these electrode chemistries. As a lithium-ion conducting polymer, polyethylene oxide (PEO) is an attractive, low-cost candidate solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) for such cells, but is known to suffer from stability issues at both the anode and cathode of the cell, as well as from sluggish ion transport in the bulk. Here we consider a general approach to create stable SPEs based on PEO by redesigning the salt—as opposed to the more common practice of manipulating the polymer, to achieve SPEs that provide the right balance of transport and stability characteristics to enable solid-state batteries. We show in particular that a trinal salt mixture composed of task-specific components specifically chosen to address the three most stubborn problems of PEO-based SPEs facilitates stable cycling of Li‖LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2-NCM (111) cells, with a coulombic efficiency of 99%. Our studies shed light on a potentially new approach for rationally designing the interphases at both the cathode and anode of solid polymer batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...