Azobenzene based inorganic salts for light modulated ionic conductivity in aqueous solution†
Abstract
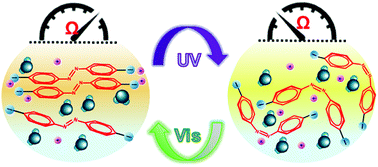
Azobenzene based inorganic salts containing lithium, sodium or potassium cations were prepared and the behaviors of reversible light modulated ionic conductivity were observed based on photoisomerizations of azobenzene salts in aqueous solutions. The highest ionic conductivity was observed in the solution of potassium ionized azobenzene, assisted by the unique formation of a network-like aggregated morphology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...