Force fluctuations at the transition from quasi-static to inertial granular flow†
Abstract
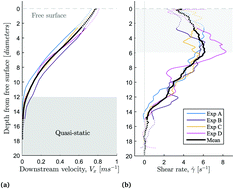
We analyse the rheology of gravity-driven, dry granular flows in experiments where individual forces within the flow bulk are measured. We release photoelastic discs at the top of an incline to create a quasi-static erodible bed over which flows a steady 2D avalanche. The flowing layers we produce are dense (ϕ ≈ 0.8), thin (h ≈ 10d), and in the slow to intermediate flow regime (I = 0.1 to 1). Using particle tracking and photoelastic force measurements we report coarse-grained profiles for packing fraction, velocity, shear rate, inertial number, and stress tensor components. In addition, we define a quantitative measure for the rate of generation of new force chain networks and we observe that fluctuations extend below the boundary between dense flow and quasi-static layers. Finally, we evaluate several existing definitions for granular fluidity, and make comparisons among them and the behaviour of our experimentally-measured stress tensor components. Our measurements of the non-dimensional stress ratio μ show that our experiments lie within the local rheological regime, yet we observe rearrangements of the force network extending into the quasi-static layer where shear rates vanish. This elucidates why non-local rheological models rely on the notion of stress diffusion, and we thus propose non-local effects may in fact be dependent on the local force network fluctuation rate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...