Tuning gelled lyotropic liquid crystals (LLCs) – probing the influence of different low molecular weight gelators on the phase diagram of the system H2O/NaCl–Genapol LA070
Abstract
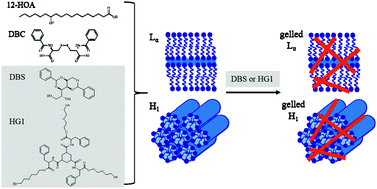
Gelled lyotropic liquid crystals (LLCs) are highly tunable multi-component materials. By studying a selection of low molecular weight gelators (LMWGs), we find gelators that form self-assembled gels in LLCs without influencing their phase boundaries. We studied the system H2O/NaCl–Genapol LA070 in the presence of (a) the organogelators 12-hydroxyoctadecanoic acid (12-HOA) and 1,3:2,4-dibenzylidene-D-sorbitol (DBS) and (b) the hydrogelators N,N′-dibenzoyl-L-cystine (DBC) and a tris-amido-cyclohexane derivative (HG1). Visual phase studies and oscillation shear frequency sweeps confirmed that 12-HOA acts as co-surfactant (stabilizing the lamellar Lα phase and destabilizing the hexagonal H1 phase), thus preventing gelation. Conversely, DBS was a potent gelator for LLCs, with the phase boundaries un-influenced by the presence of DBS; gelled lamellar Lα, and softly-gelled hexagonal H1 phases are formed. For the hydrogelator DBC, the LLC phase boundaries were only slightly altered, but no gelled LLCs were formed. For the hydrogelator HG1, however, the phase boundaries were unaffected while gelled lamellar Lα and softly-gelled hexagonal H1 phases were formed. Temperature-dependent rheology measurements demonstrated that by changing the DBS or the HG1 concentration, the sol–gel transition temperature of the gelled lamellar Lα phase can be adjusted such that (a) Tsol–gel is below the Lα-isotropic phase transition (DBS, HG1 mass fraction η = 0.0075) and (b) Tsol–gel is above the gelled Lα-isotropic phase transition (DBS, HG1 η = 0.015). This opens the possibility of temporal materials control by addressing phase transitions in different orders. As this system contains oil and water, both the organogelator DBS and the hydrogelator HG1 can gel these LLCs, but this clearly does not apply to all organogelators/hydrogelators. The study indicates that careful optimization of LMWGs is required to avoid interaction with the surfactant layer and to optimize the Tsol–gel value, which is important for the application of LMWGs in gelled LLCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...