Luminescence down-shifting enables UV-stable and efficient ZnO nanowire-based PbS quantum dot solar cells with JSC exceeding 33 mA cm−2†
Abstract
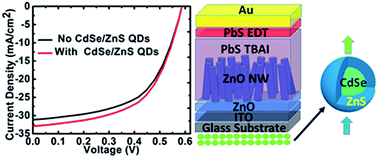
Solar cells with a PbS quantum dot (QD) active layer are promising candidates for the next generation of low-cost and efficient solution-processed photovoltaic (PV) devices due to their direct and tunable bandgap, air stability and facile fabrication process. In fact, PbS QD PVs rely on replacing the long oleate ligands with shorter bidentate or halide-based atomic ligands that alter their energy levels with enhanced surface passivation. Such shorter organic ligands are typically sensitive to ultraviolet (UV) radiation present in the solar spectrum. Therefore, under illumination, they are prone to degradation, decomposition or detachment from the QD surface, ultimately leading to degraded PV performance. So far, the impact of UV irradiation on the PbS QD device has not been studied. Here, the impact of long durations of UV-exposure on exchanged PbS QD films was studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). We employ an effective strategy to enhance the UV stability of PbS QD solar cells using a luminescence down-shifting CdSe/ZnS QD layer deposited on the back of the device structure. Moreover, we find that using this technique, the incoming UV photons that would not normally contribute to carrier generation – due to absorbance by other layers or energy thermalization in the PbS QD absorber layer – are absorbed and re-emitted at a visible wavelength leading to enhanced carrier generation. By optimizing and combining this luminescence down-shifting strategy with an ordered bulk heterojunction (OBHJ) architecture consisting of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanowires (NWs), UV-stable and efficient PbS QD solar cells are achieved. Our best performing device shows a record high short-circuit current density (JSC) of 33.2 mA cm−2 and power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 10.62%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...