Photoelectrochemical-voltaic cells consisting of particulate ZnxCd1−xSe photoanodes with photovoltages exceeding 1.23 V†
Abstract
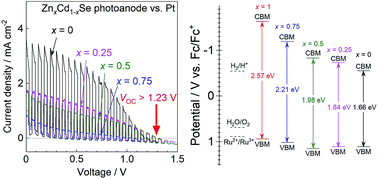
Photoelectrochemical-voltaic (PECV) cells generating photovoltages higher than the thermodynamic onset voltage for water splitting (1.23 V) with a one-step bandgap photoexcitation can be constructed using particulate ZnxCd1−xSe photoanodes in a nonaqueous electrolyte. The alloys of ZnSe and CdSe show tunable and intense visible-light absorption in the wavelength region ranging from 480–750 nm according to the Zn/Cd ratio, although the materials are incapable of directly splitting water due to photocorrosion. A PECV cell consisting of a Zn0.25Cd0.75Se photoanode and a Pt black cathode in an acetonitrile electrolyte containing Ru(bpy)32+/3+ complexes as a redox pair exhibits a photovoltage of 1.32 V and a relatively high anodic photocurrent of 1.7 mA cm−2 under simulated sunlight. The obtained photovoltage is consistent with the difference between the onset potential of the photoanode and redox equilibrium potential in the nonaqueous electrolyte, and is equivalent to as high as 72% bandgap energy for Zn0.25Cd0.75Se, i.e., 1.84 eV. The concepts of the present PECV cells will open a new way for converting a large portion of the bandgap energy into photovoltage, and splitting water using semiconductor materials unstable in water.
- This article is part of the themed collections: 2019 Sustainable Energy and Fuels HOT Articles and 3rd International Solar Fuels Conference and International Conference on Artificial Photosynthesis


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...