Capture and conversion of carbon dioxide by solar heat localization†
Abstract
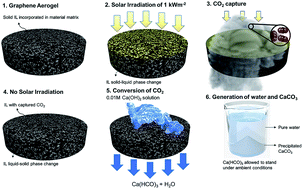
As the world slowly transitions from conventional fossil fuels to renewable forms of energy, environmentally friendly CO2 capture is urgently needed. Currently, liquid amine and ionic liquid-based systems are utilized for this purpose. However, these forms of capture mostly lead to the formation of stable carbamate salts with high enthalpy of formation, and it is therefore difficult to recover the initial liquid for cyclic operation. Furthermore, amine-based technologies pose concerns including toxic emissions and volatility, while ionic liquid-based systems suffer from complexity of liquid handling and high operational cost. Herein, we report a solid-state sustainable CO2 collector (SCC), which is activated by solar heat localization. This stable cyclic SCC is based on ionic liquids and graphene aerogel, which undergoes solid–liquid phase change to efficiently capture and convert CO2. The SCC captures 0.2 moles of CO2 for every mole of ionic liquid and converts the absorbed CO2 into useful byproducts, including water and calcium carbonate in each cycle. A system prototype of the SCC is developed and demonstrated. The SCC provides a new and promising paradigm to efficiently capture and convert CO2 using abundant solar energy to address global emissions and consequent environmental challenges.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...