Probing the reversibility and kinetics of Li+ during SEI formation and (de)intercalation on edge plane graphite using ion-sensitive scanning electrochemical microscopy†
Abstract
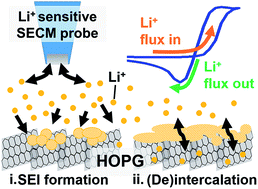
Ions at battery interfaces participate in both the solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation and the subsequent energy storage mechanism. However, few in situ methods can directly track interfacial Li+ dynamics. Herein, we report on scanning electrochemical microscopy with Li+ sensitive probes for its in situ, localized tracking during SEI formation and intercalation. We followed the potential-dependent reactivity of edge plane graphite influenced by the interfacial consumption of Li+ by competing processes. Cycling in the SEI formation region revealed reversible ionic processes ascribed to surface redox, as well as irreversible SEI formation. Cycling at more negative potentials activated reversible (de)intercalation. Modeling the ion-sensitive probe response yielded Li+ intercalation rate constants between 10−4 to 10−5 cm s−1. Our studies allow decoupling of charge-transfer steps at complex battery interfaces and create opportunities for interrogating reactivity at individual sites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...