Discovery of small-molecule inhibitors targeting the ribosomal peptidyl transferase center (PTC) of M. tuberculosis†
Abstract
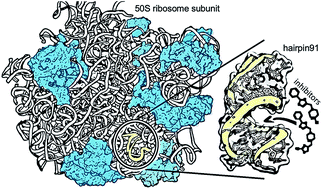
M. tuberculosis (Mtb) is a pathogenic bacterium that causes tuberculosis, which kills more than 1.5 million people worldwide every year. Strains resistant to available antibiotics pose a significant healthcare problem. The enormous complexity of the ribosome poses a barrier for drug discovery. We have overcome this in a tractable way by using an RNA segment that represents the peptidyl transferase center as a target. By using a novel combination of NMR transverse relaxation times (T2) and computational chemistry approaches, we have obtained improved inhibitors of the Mtb ribosomal PTC. Two phenylthiazole derivatives were predicted by machine learning models as effective inhibitors, and this was confirmed by their IC50 values, which were significantly improved over standard antibiotic drugs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...