Structure and effective charge characterization of proteins by a mobility capillary electrophoresis based method
Abstract
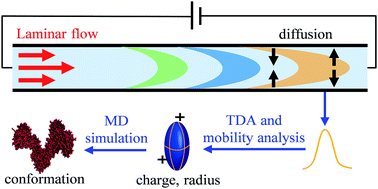
Measuring the conformations and effective charges of proteins in solution is critical for investigating protein bioactivity, but their rapid analysis remains a challenging problem. Here we report a mobility capillary electrophoresis (MCE) based method for the rapid analysis of protein stereo-structures and effective charges in different solution environments. With the capability of mixture separation, MCE measures the hydrodynamic radius of a protein through Taylor dispersion analysis and its effective charge through ion mobility analysis. The experimental results acquired from MCE are then utilized to restrain molecular dynamics simulations, so that the most probable conformation of that protein can be obtained. As proof-of-concept demonstrations, the charge states and structures of five proteins were analyzed under close to native environments. The conformation transitions and charge state variations of bovine serum albumin and lysozyme under different pH conditions were also investigated. This method is promising for high-throughput protein analysis, which could potentially be coupled with mass spectrometry for investigating protein stereo-structures and functions in top-down proteomics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...