Stereoisomerism of stapled peptide inhibitors of the p53-Mdm2 interaction: an assessment of synthetic strategies and activity profiles†
Abstract
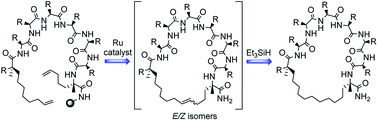
All-hydrocarbon, i, i+7 stapled peptide inhibitors of the p53-Mdm2 interaction have emerged as promising new leads for cancer therapy. Typical chemical synthesis via olefin metathesis results in the formation of both E- and Z-isomers, an observation that is rarely disclosed but may be of importance in targeting PPI. In this study, we evaluated the effect of staple geometry on the biological activity of five p53-reactivating peptides. We also present strategies for the modulation of the E/Z ratio and attainment of the hydrogenated adduct through repurposing of the metathesis catalyst.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...