Sacrificial oxidation of a self-metal source for the rapid growth of metal oxides on quantum dots towards improving photostability†
Abstract
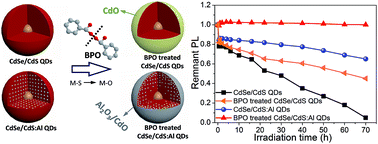
Growth of metal oxide layers on quantum dots (QDs) has been regarded as a good way to improve the photostability of QDs. However, direct growth of metal oxides on individual QD remains a great challenge. Here we report a novel approach to rapidly anchor metal oxides on QD surfaces through a sacrificial oxidation of a self-metal source strategy. As typical core/shell QDs, CdSe/CdS or aluminum doped CdSe/CdS (CdSe/CdS:Al) QDs were chosen and treated with peroxide (benzoyl peroxide). Self-metal sources (cadmium or/and aluminum) can be easily sacrificially oxidized, leading to the quick growth of cadmium oxide (CdO) or aluminum/cadmium hybrid oxides (Al2O3/CdO) on the surface of individual QD for improved photostability. Compared with CdO, Al2O3 possesses excellent barrier properties against moisture and oxygen. Therefore, CdSe/CdS QDs with the protection of an Al2O3/CdO hybrid layer show much superior photostability. Under strong illumination with blue light, the QDs coated with the Al2O3/CdO hybrid layer retained 100% of the original photoluminescence intensity after 70 h, while that of the untreated CdSe/CdS:Al, the treated CdSe/CdS and the CdSe/CdS QDs dropped to 65%, 45%, and 5%, respectively. Furthermore, we demonstrate that this method can be extended to other metal-doped QD systems, even including some inactive metals difficult to be oxidized spontaneously in an ambient atmosphere, which provides a new way to stabilize QDs for diverse optoelectronic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...