Dependence of the fluorination intercalation of graphene toward high-quality fluorinated graphene formation†
Abstract
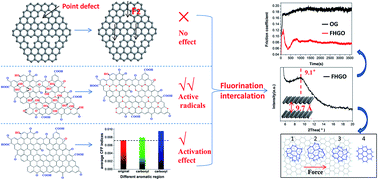
A direct gas–solid reaction between fluorine gas (F2) and graphene is expected to become an inexpensive, continuous and scalable production method to prepare fluorinated graphene. However, the dependence of the fluorination intercalation of graphene is still poorly understood, which prevents the formation of high-quality fluorinated graphene. Herein, we demonstrate that chemical defects (oxygen group defects) on graphene sheets play a leading role in promoting fluorination intercalation, whereas physical defects (point defects), widely considered to be an advantage due to more diffusion channels for F2, were not influential. Tracing the origins, compared with the point defects, the unstable hydroxyl and epoxy groups produced active radicals and the relatively stable carbonyl and carboxyl groups activated the surrounding aromatic regions, thereby both facilitating fluorination intercalation, and the former was a preferential and easier route. Based on the above investigations, we successfully prepared fluorinated graphene with an ultrahigh interlayer distance (9.7 Å), the largest value reported for fluorinated graphene, by customizing graphene with more hydroxyl and epoxy groups. It presented excellent self-lubricating ability, with an ultralow interlayer interaction of 0.056 mJ m−2, thus possessing a far lower friction coefficient compared with graphene, when acting as a lubricant. Moreover, it was also easy to exfoliate by shearing, due to the diminutive interlayer friction and eliminated commensurate stacking. The exfoliated number of layers of less than three exceeded 80% (monolayer rate ≈ 40%), and no surfactant was applied to prevent further stacking.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...