Cyclometalated iridium–BODIPY ratiometric O2 sensors†
Abstract
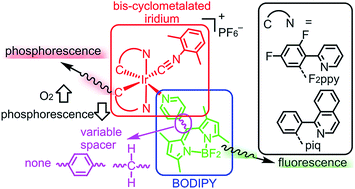
Here we introduce a new class of ratiometric O2 sensors for hypoxic environments. Two-component structures composed of phosphorescent cyclometalated Ir(III) complexes and the well-known organic fluorophore BODIPY have been prepared by the 1 : 1 reaction of bis-cyclometalated iridium synthons with pyridyl-substituted BODIPY compounds. Two different cyclometalating ligands are used, which determine the relative energies of the iridium-centered and BODIPY-centered excited states, and the nature of the linker between iridium and BODIPY also has a small influence on the photoluminescence. Some of the conjugates exhibit dual emission, with significant phosphorescence from the iridium site and fluorescence from the BODIPY, and thus function as ratiometric oxygen sensors. Oxygen quenching experiments demonstrate that as O2 is added the phosphorescence is quenched while the fluorescence is unaffected, with dynamic ranges that are well suited for hypoxic sensing (pO2 < 160 mmHg).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...